Bitcoin-style ledgers expose sender links, recipient links, and transferred value. Addresses appear anonymous, but transaction behavior creates identifiable patterns. Modern chain analytics defeat pseudonymity by combining exchange records, timing correlations, and address clustering, turning public blockchains into permanent financial records tied to behavior rather than names.
In this article, a market-and-tech review covers privacy coins researching how transaction secrecy functions at the protocol level, where real adoption stands in 2026, and why exchange access continues shrinking for networks offering uncompromising privacy.
Privacy coins hide three things:
Sender linkage (who spent)
Recipient linkage (who received)
Amount visibility (how much moved)

Bitinfo Comparison of Privacy coins vs Bitcoin
Monero (XMR) Privacy Tech: Ring Signatures, Stealth Addresses, RingCT Amount Hiding
Monero runs privacy as default behavior. Every transfer uses a bundle of techniques:
Ring signatures: the spend blends among decoys, blocking clean input attribution.
Stealth addresses: each payment lands on a one-time destination, blocking direct recipient mapping.
RingCT: Pedersen commitments plus range proofs hide values while preserving balance correctness.
As a result, Monero delivers strong ledger-level confidentiality at the cost of heavier transactions and increased on-chain data compared to transparent systems.
Coinmarket Cap Privacy Coins
Market snapshot: XMR carries a market capitalization of roughly $7.9B–$8.0B.
Regulatory reality: Mandatory privacy conflicts directly with compliance frameworks built on transaction traceability. Monero provides no protocol mechanism for forced counterparty disclosure at transfer time.
Zcash (ZEC) Privacy Tech: zk-SNARK Shielded Transfers and Viewing Keys
Zcash has some of the strongest privacy technology amongst the altcoins—but only when shielded transactions are actually used. zk-SNARKs allow transfers to be verified without revealing who sent the funds, who received them, or how much moved.
Viewing keys make it possible to share transaction details selectively with auditors or counterparties.
The problem is in adoption. Most Zcash activities do not use shielded pools. Public data shows shielded transactions make up only a minority of total usage, with recent estimates placing adoption around 15–20% in 2025, depending on how it’s measured.
Market snapshot: ZEC holds a market capitalization of roughly $8.6B–$8.75B (as of December 29, 2025).
Dash (DASH) Privacy Tech: PrivateSend Mixing With Mostly Transparent Activity
Dash does not offer ledger-level privacy. Dash holds a PrivateSend feature that relies on CoinJoin-style mixing coordinated by masternodes, but transaction amounts and output addresses remain visible on-chain even after mixing.
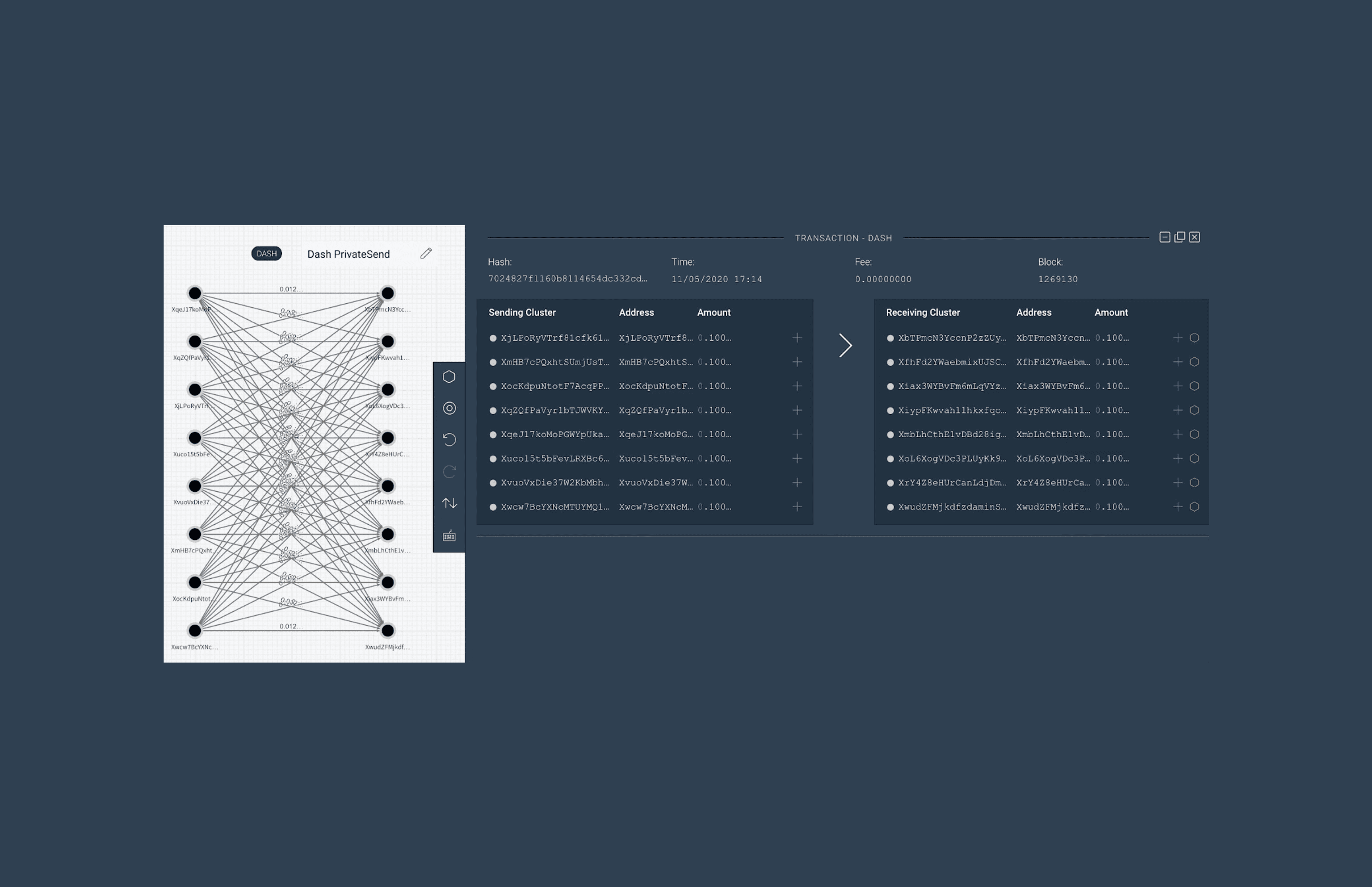
Dash PrivateSend
Example of a Dash PrivateSend mix: eight inputs of 0.1 DASH are pooled and reshuffled into eight outputs of 0.1 DASH, with each participant receiving one corresponding output.
Usage is minimal. Chainalysis data shows that PrivateSend accounts for less than 0.7% of Dash transactions. The overwhelming majority of activity on the network consists of fully transparent transfers.
Market snapshot: DASH carries a market capitalization of roughly $532M–$534M (as of December 29, 2025).
Mimblewimble Privacy: Litecoin MWEB
Mimblewimble (MWEB) removes classic address formats, aggregates transactions, and hides amounts via commitments. Litecoin’s MWEB also supports pruning, shrinking chain bloat.
Litecoin MWEB: Privacy Add-On, Not a Separate Coin
MWEB adds optional confidential transfers inside an extension environment while Litecoin base-layer activity remains transparent. Optional design avoids “privacy-only chain” branding, but optional design also means privacy usage depends on wallet and user behavior.
Coordination Without Exposure: Canton Network
Canton Network enables shared transaction coordination while keeping sensitive financial data private. Instead of broadcasting trades, balances, and strategies to a global ledger, Canton restricts visibility to only the parties involved, with regulators granted scoped access when required.
Global Synchronization Without Data Access
At the core of Canton Network is the Global Synchronizer, which orders and timestamps transactions without seeing their contents. This design allows assets and payments to move across firms without exposing commercial activity or creating centralized points of control.
Privacy Coins Comparison Table: Market Cap, Privacy Usage, Exchange Access, Regulatory Status
Asset | Ledger privacy model | Market cap (screenshots, 2025-12-29) | Privacy usage rate | Exchange listings (count sources) | Regulatory status snapshot |
Monero (XMR) | Mandatory privacy | ~$7.6B–$8.0B | Default on-chain | ~30 exchanges (count source) CoinCodex | Heavily restricted; EEA Kraken support ended Kraken Support |
Zcash (ZEC) | Optional shielded | ~$8.6B–$8.75B | ~15–20% shielded (source) Sparkco | ~69 exchanges (count source) CoinCodex | Mixed availability; less friction than XMR |
Dash (DASH) | Optional mixing | ~$532M–$534M | <0.7% PrivateSend transfers Chainalysis | ~55 exchanges (count source) CoinCodex | Generally more tolerated than XMR |
Verge (XVG) | IP masking only | not provided | Ledger transparent | not provided | Security history harms credibility |
Market Reality Check: Exchange Access Is the Story
Liquidity sits on regulated exchanges, and privacy assets keep getting removed. During 2024, centralized platforms accelerated delistings of privacy-focused tokens, reaching the highest level in years.
Industry data shows close to 60 privacy-token delistings in 2024. Monero absorbed the largest share, with removals multiplying year over year. Dash followed behind. Enforcement pressure, not technical failure drives the trend.
Regulation Pushes Privacy Coins Off Mainstream Exchanges
Regulatory action explains the shift.
Regulatory pressure: Privacy tokens face outright bans or effective restrictions in Japan, South Korea, Australia, the UAE, and across Europe under MiCA.
Exchange response: Large platforms reduced exposure rather than fight enforcement risk, leading to removals such as Kraken disabling XMR in Europe and Binance delisting Monero.
Liquidity shift: Trading activity migrated to lightly regulated venues, now handling roughly 40% of privacy-token volume with thinner order books.
Market takeaway: Exchange access now matters more than cryptographic design as regulatory constraints tighten.
Real Usage: Remittances, Business Payments, Activism, Donations
Most “privacy coin use cases” read larger than observed volume on regulated venues. Market behavior shows speculation and trading as the dominant activity.
Remittances: Real usage exists, mostly outside fully regulated rails; scale data remains fragmented and often off-exchange.
Business confidentiality: Niche usage, usually for counterparties who already operate in altcoin-native circles.
Activism and civil-society funding: Real in pockets, but not mass retail scale; operational security dominates outcomes more than coin choice.
Political donations: Sporadic and jurisdiction-dependent; accountability laws limit open deployment.
Risks of Privacy Coins Compared to Bitcoin
Regulatory Risk: Privacy coins face higher scrutiny and exchange delistings due to default transaction obfuscation, while Bitcoin’s transparent ledger is broadly accepted by regulators.
Liquidity Risk: Privacy coins often have thinner markets and fewer fiat on-ramps, whereas Bitcoin benefits from deep global liquidity and institutional-grade market infrastructure.
Compliance Risk: Default privacy can make it difficult for institutions, funds, and custodians to meet AML, audit, and reporting requirements, limiting adoption compared to Bitcoin.
Network Effect Risk: Bitcoin’s first-mover advantage, brand recognition, and widespread integration create a reinforcing adoption loop that most privacy coins struggle to match.
Protocol Risk: Advanced cryptography used in privacy coins increases complexity and long-term maintenance risk, while Bitcoin’s simpler and well-tested design prioritizes robustness and stability.
Conclusion
Regulators require exchanges to identify who sends and who receives funds for certain transactions. This rule is based on the expectation that blockchains can, in certain circumstances, make transaction counterparties identifiable.
Privacy coins like Monero do the opposite. Transaction data is hidden by design. Sender and receiver information never appears on-chain, and the protocol does not allow forced disclosure when a transaction is broadcast. Monero cannot meet Travel Rule requirements at the protocol (Layer 1) level. The base layer does not produce counterparty information, and there is no mechanism to selectively disclose it.
Optional privacy coins like Zcash do appear to have slightly better regulatory standing than mandatory-privacy coins like Monero, but they're still facing severe pressure and widespread delistings. The statement oversimplifies a complex and evolving situation.
자주 묻는 질문
면책 조항
이 글에 제공된 정보는 정보 제공을 위한 것입니다. 이는 금융 자문으로 간주되어서는 안 되며, 금융 자문을 의미하지 않습니다. 우리는 이 정보의 완전성, 신뢰성, 정확성에 대해 어떠한 보증도 하지 않습니다. 모든 투자는 위험을 수반하며 과거의 실적이 미래의 결과를 보장하지 않습니다. 투자 결정을 내리기 전에 금융 자문가와 상담할 것을 권장합니다.

















